SARK V4.0.0 Exten
Contents
Adding Extensions
Extensions for the FXS channels are already defined in the system when it leaves the factory. There is nothing further to do. However, you will almost certainly want to define SIP extensions to the system. If you have SIP Multicast (sometimes called PnP) capable handsets you can use SARK500's ZTP auto-configure feature to set up your phones (see the ZTP/PnP section below). For non-PnP-capable handsets you can add new extensions using the extensions panel ...
To add an extension; click extensions at the top of the navigation menu. Then click the “new” button to create an extension.
Choose the phone type from the device drop-down. Fill out the details for your phone and (optionally) enter the MAC address if you want SARK to automagically generate a TFTP provisioning file for your phone type. SARK has a fairly extensive phone database and it can provision most commercially available phone types. When it generates the sip.conf entries, SARK will create a random password for each extension. Additionally, if you turn on ACL checking in globals, SARK will also include the correct ACL checking for your subnet in the sip.conf entry.
what does SARK generate for each extension?
You can examine and modify the SARK generated output by clicking the edit button next to the phone entry in the extensions panel and then clicking the Asterisk or Provisioning tabs on the edit panel. On examining these panels you will see that SARK uses symbolic names for some of the entries. These symbolic names begin with a $ sign. SARK uses late resolution for t these symbolic values which means that it only resolves them at the point of usage and not in the SARK database. In practice, this allows a greater level of flexibility and security but you can, if you wish, override any of the entries with your own permanent values, although it is usually better to leave them to SARK to manage.
Asterisk edit
Provisioning edit
SARK will generate phone specific provisioning data for each phone type it recognises. Most popular SIP phone models are recognised by SARK but the provisioning sub-system is open-ended so you can create your own provisioning templates for phone types that aren't natively supported. For more information on provisioning templates see the relevant section in the wiki. The example below shows provisioning data for a SNOM 320.
Dynamic Proxy
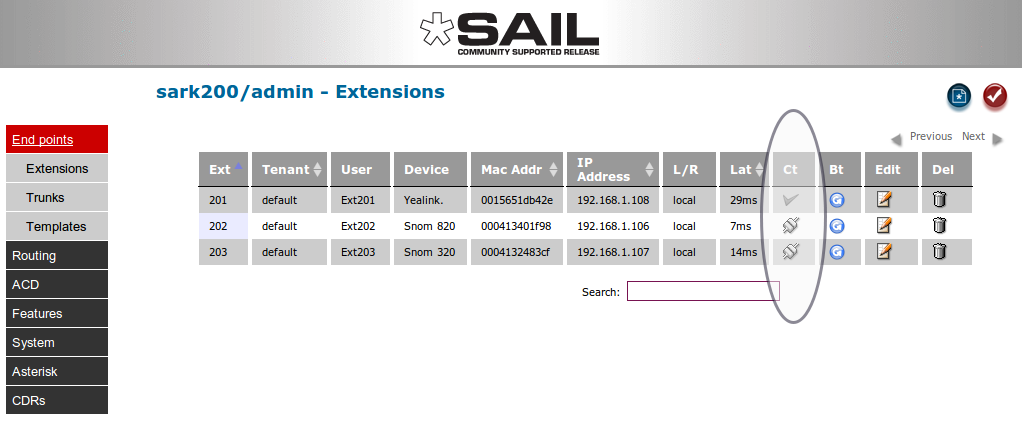
For locally attached extensions which support browser proxying, SARK extension edit provides a passthru mode to interact directly with the phone. In order for this feature to work you must first enable dynamic proxy in the Globals panel. SARK cannot normally proxy to remote phones however it is possible for phones which support VPN, e.g. Snom370 & Snom870. There are also phone types which do not "play well" with proxy browsing, for example Yealink. For this reason, SARK sets an icon in the "Ct" (Connect) column to indicate whether a phone is on-line and also, whether a proxy can be attempted. If the phone is off-line then the cell will contain "N/A", if it is online but not available for browsing it will show as a checkmark (tick) and if it is online and can be proxied it will show a connected icon.
In the example above, SARK has set the Yealink phone ct icon to a checlmark because the browser on Yealink phones does not proxy well. However, the two Snoms are both showing as available. To proxy to the phone click on the connected icon. SARK will procy to the phone and display the output in the SARK data window.
This is very useful if you need to log in to a remote SARK instance and then log in to a particular phone to make a change or check a setting on-the-fly. Supported phones are; all Snom, Aastra, Grandstream and Polycom variants and all Cisco small business phones (formerly linksys/Sipura) with one or two restrictions on Sipura devices (some features may not work in the browser). Yealink phones are not supported and there is only partial support for Gigaset devices.